European countries led the way to the New World due to superior technology, navigation skills, and resources. This allowed them to establish colonies, conduct trade, and expand their empires.
The Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries saw European powers like Spain, Portugal, England, and France compete for territory and resources in the Americas. Their advancements in shipbuilding, mapmaking, and weaponry gave them a significant advantage over indigenous populations.
European explorers sought new trade routes, wealth, and opportunities for expansion, ultimately shaping the course of world history. This period marked a pivotal moment in global exploration and colonization, with lasting impacts on cultures, economies,
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration, was a period from the early 15th century to the early 17th century when European powers embarked on a series of maritime expeditions to explore, trade, and colonize new lands. This era was characterized by significant advancements in navigation, technology, and cartography, which enabled European countries to lead the way to the New World.
Early Maritime Exploits
European nations, including Portugal, Spain, England, France, and the Netherlands, sought new trade routes to access valuable goods from Asia and Africa. This quest for alternative tr
Technological Advancements
During the Age of Discovery, advancements in shipbuilding, navigation tools, and cartography played a crucial role in facilitating transatlantic voyages. The development of more seaworthy vessels, such as the caravel, improved the ability to withstand long journeys, while the astrolabe and magnetic compass aided navigators in determining their position at sea. Additionally, the refinement of mapmaking techniques and the introduction of the printing press allowed for the dissemination of accurate navigational charts and geographical knowledge, further propelling European exploration.
Motivations Behind Explorations
European exploration of the New World was driven by a complex mix of motivations that propelled countries to expand their reach beyond their own borders. The motivations behind these explorations can be categorized into three main factors: economic ambitions, religious zeal, and political rivalries. Each of these factors played a significant role in shaping the course of history and the eventual colonization of the New World.
Economic Ambitions
The pursuit of wealth and trade opportunities drove European nations to seek new routes to the East and discover untapped resources in the New World. The desire to establish direct trade links with Asia and access valuable commodities such as spices, silk, and precious metals fueled the exploration efforts. In addition, European powers sought to establish lucrative colonial enterprises and expand their influence to gain a competitive edge in the global economy.
Religious Zeal
Religious fervor and the quest for spiritual dominance were powerful driving forces behind the exploration of the New World. European nations, particularly Spain and Portugal, sought to spread Christianity and convert indigenous populations to their faith. The idea of religious conquest and the expansion of the Christian faith drove explorers and missionaries to venture into unknown territories, leading to the establishment of missionary outposts and the conversion of indigenous peoples.
Political Rivalries
Intense competition among European powers for territorial expansion and political supremacy fueled the race to the New World. Rivalry between nations such as Spain, Portugal, England, France, and the Netherlands drove them to stake their claims in the New World, leading to the establishment of colonial settlements and the assertion of political control. The pursuit of strategic advantages and the desire to outdo rival powers spurred explorers to navigate uncharted waters and establish footholds in the New World.
Key Figures In New World Expeditions
The exploration and colonization of the New World by European countries during the Age of Discovery was led by a number of key figures who played pivotal roles in these expeditions. Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan were among the most prominent explorers who ventured into the unknown, paving the way for the European domination of the New World. Let’s take a closer look at each of these influential figures and their contributions.
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus, an Italian explorer sailing under the Spanish flag, is widely credited with discovering America in 1492. Columbus embarked on his historic expedition in search of a western route to Asia, but instead stumbled upon the Caribbean islands and the American continent. His voyages opened up a new era of transatlantic exploration and colonization, forever altering the course of history.
Vasco Da Gama
Vasco da Gama, a Portuguese explorer, is renowned for being the first European to reach India by sea. In 1498, da Gama successfully sailed around the Cape of Good Hope, opening up a direct maritime trade route between Europe and Asia. His voyage not only established Portugal’s dominance in the lucrative spice trade but also paved the way for further European exploration and colonization in the East Indies.
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer sailing under the Spanish flag, is best known for leading the first circumnavigation of the globe. In 1519, Magellan set sail with a fleet of ships to find a western route to the Spice Islands. Although he did not survive the entire journey, his expedition proved that it was possible to sail around the world. Magellan’s voyage marked a significant milestone in European exploration and demonstrated the vastness of the Earth. These key figures in New World expeditions were driven by a thirst for knowledge, a desire for wealth and power, and the spirit of adventure. Their bold and daring voyages not only expanded Europe’s understanding of the world but also laid the foundations for the future colonization and development of the New World.

Credit: study.com
Impact Of The Renaissance
The Renaissance, a period of cultural and intellectual rebirth in Europe from the 14th to the 17th century, had a profound impact on the European countries’ drive to explore and lead the way to the New World. This transformative era brought about significant changes in various aspects of society, including humanism and curiosity, as well as scientific innovations.
Humanism And Curiosity
Humanism, a philosophical movement that emphasized the potential and worth of human beings, played a crucial role in driving European countries towards exploration. During the Renaissance, there was a renewed interest in classical knowledge and the study of ancient texts. This intellectual curiosity fueled a thirst for exploration and discovery beyond the boundaries of Europe. The humanist philosophy encouraged individuals to question existing beliefs and explore new ideas, leading to an increased sense of curiosity about the world. This curiosity, combined with the desire to expand trade routes and acquire valuable resources, motivated European countries to venture into uncharted territories.
Scientific Innovations
The Renaissance also witnessed significant scientific advancements that further propelled European countries towards exploration. The era saw groundbreaking discoveries in various fields, including astronomy, navigation, and cartography.
The Role Of Monarchies
Royal Patronage
In the race to the New World, European monarchies played a crucial role through their royal patronage. They provided financial and logistical support to explorers and expeditions, fueling the maritime exploration that ultimately led to the discovery and colonization of the Americas.
Consolidation Of Power
Another pivotal aspect was the consolidation of power by European monarchies. As they sought to expand their influence and wealth, they financed and endorsed ambitious voyages to seek new trade routes and territories, driving the age of exploration.

Credit: www.pewresearch.org
Navigational Tools And Techniques
Navigational tools and techniques played a crucial role in the European countries’ expeditions to the New World.
The Astrolabe And Compass
The astrolabe and compass were essential tools for determining latitude and direction at sea. Sailors used the astrolabe to measure the angle between the sun or a star and the horizon, aiding in navigation. The compass, with its magnetic needle pointing north, helped sailors maintain their course, especially in overcast weather or at night.
Cartography And Shipbuilding
Advancements in cartography, the art of mapmaking, enabled explorers to create more accurate charts of their voyages. These maps helped them navigate unknown waters with greater precision. In shipbuilding, innovations like the caravel allowed for faster and more maneuverable vessels, essential for long-distance journeys.
Economic Systems And Trade
European countries led the way to the New World due to advanced economic systems and trade networks.
European countries led the way to the New World due to their advanced economic systems and trade practices.
The Spice Trade
The Spice Trade drove European exploration due to the high demand for spices.
Mercantilism And Colonies
Mercantilism led European nations to establish colonies for economic gain.
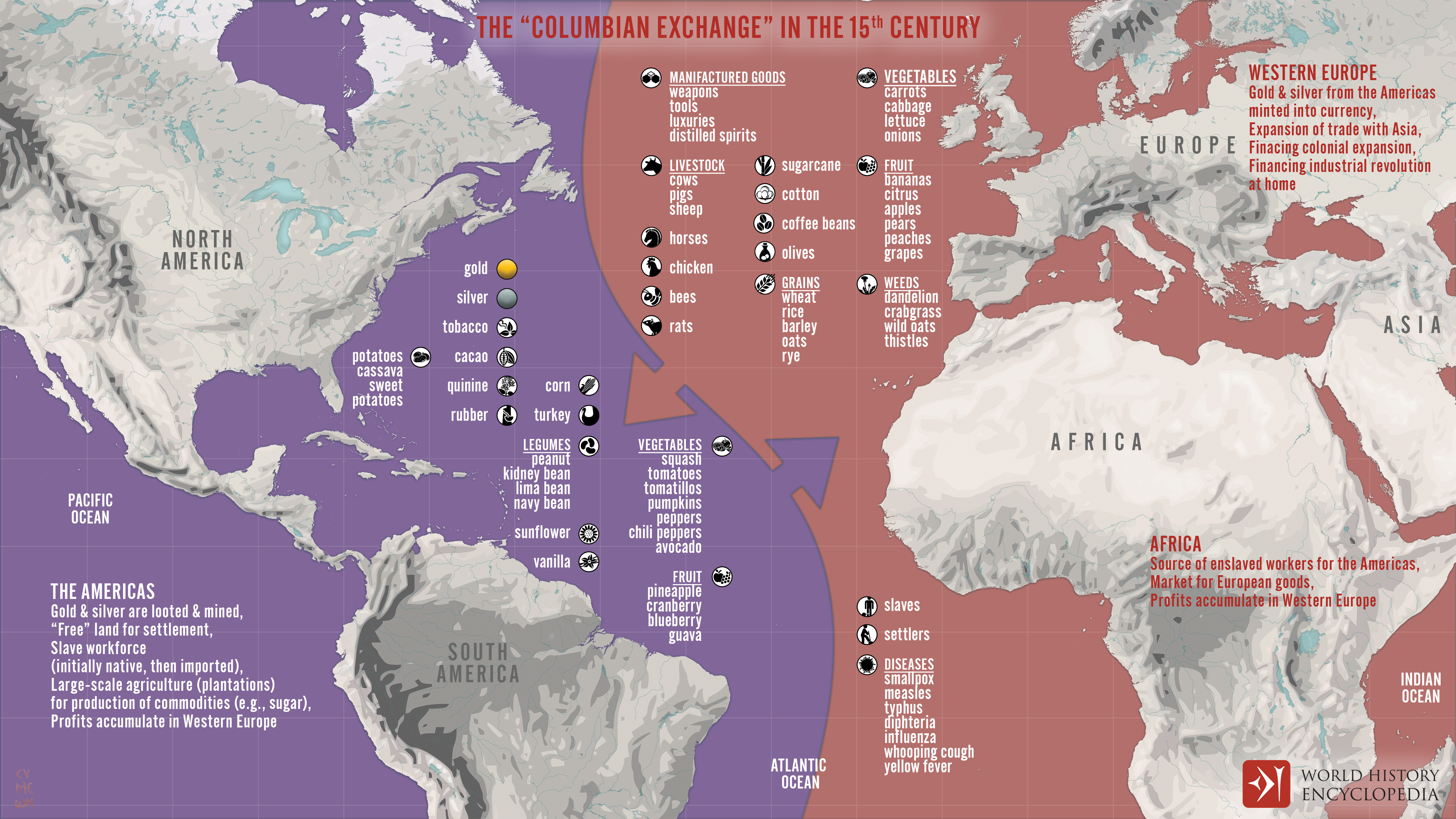
Credit: www.worldhistory.org
Consequences Of European Expansion
The consequences of European expansion had far-reaching impacts on the New World, shaping its history and societies in profound ways.
Cultural Exchanges
Cultural exchanges between Europeans and indigenous peoples brought new languages, foods, and traditions to both worlds.
Colonialism And Its Legacy
Colonialism and its legacy led to the exploitation of natural resources and the imposition of European systems of governance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Factors Led European Countries To Explore And Colonize The New World?
How Did European Colonization Impact The Indigenous Populations Of The New World?
European colonization had a devastating effect on the indigenous populations of the New World.
Which European Countries Were The Most Successful In Colonizing The New World?
Spain, Portugal, France, and England were the most successful in colonizing the New World. Spain and Portugal were the first to establish colonies in the Americas, while France and England later established colonies in North America. These countries were able to establish strong economies and political systems in their colonies, leading to long-lasting impacts on the region.
Conclusion
European countries played a pivotal role in the exploration and colonization of the New World. They possessed advanced technology, strong naval power, and a desire for wealth and power.